ETICS Materials – What They Are and What You Need to Know

External thermal insulation is a multilayer system applied to the outer side of a building/house walls, aiming to improve energy efficiency and reduce heat losses.
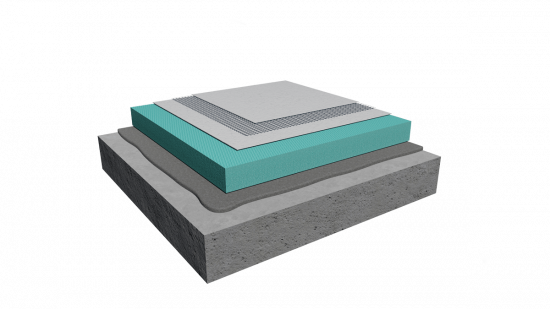
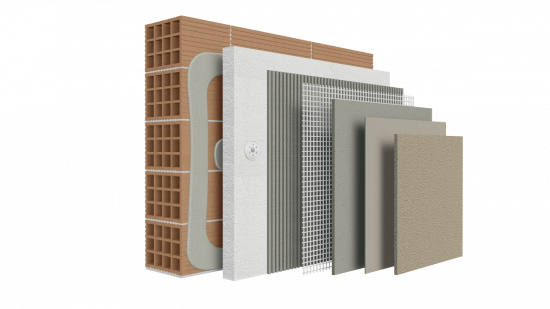
This system, also known as ETICS (External Thermal Insulation Composite System), consists of special thermal insulation boards that are installed onto the existing masonry and exposed external surfaces, and are then covered with renders (e.g. plaster or other finishing surface materials).
The purpose of the system is to create a continuous thermal insulation “cladding” that externally surrounds the structure as a protective and temperature-regulating “envelope.” With this intervention, heat loss from the interior to the outdoor environment during the cold months is prevented, while the house remains cooler in summer, as the system also forms a barrier against high external temperatures.
In this way, the home’s energy efficiency is improved, related costs are reduced, and at the same time the comfort and well-being of the occupants are enhanced.
The Main Materials of an ETICS System
Let us now look at the primary thermal insulation materials used in ETICS, focusing on Α. Thermal insulation boards (four types of insulation boards), which form the core of every modern system of this kind, and Β. Adhesive mortars and finishing renders. Finally, we must not overlook C. The auxiliary components that are essential for the proper installation of an external thermal insulation system.
Thermal Insulation Boards
Extruded Polystyrene (XPS)
Extruded Polystyrene is a synthetic thermal insulation material widely used in construction. It is produced through the continuous extrusion of polystyrene under pressure, creating a dense, closed-cell structure characterized by low thermal conductivity and excellent moisture resistance — which in practical terms means it retains its insulating properties even in humid conditions.
It is also highly resistant to mechanical loads and offers high compressive strength, making it ideal in cases where the insulation layer will be subjected to loads or pressure.
The main applications of XPS include surfaces in contact with the ground (e.g., basement walls/perimeter insulation), structural elements exposed to moisture (floors, flat roofs), areas under heavy stress, or where low water absorption is required (e.g., load-bearing concrete, common-use areas).
Expanded Polystyrene (EPS)
Expanded Polystyrene is one of the most widely used thermal insulation materials in building construction in Europe, especially in external thermal insulation systems (ETICS). It consists of boards made from polystyrene with a closed-cell structure.
EPS is widely used in the external envelope of walls (as insulation panels in ETICS), as well as in other structural applications such as roofs, basement walls, ceilings, and floor insulation layers. Its broad use is due to its low cost, light weight, ease of processing and installation, and its long-term stable insulating performance when properly installed.
EPS panels are available in various densities and thicknesses, allowing engineers to select the most suitable solution depending on energy performance requirements and the type of construction. It is relatively resistant to moisture, maintains stable thermal insulation performance over time, and is a primary choice for ETICS applications thanks to its affordability and ease of handling.
Graphite Expanded Polystyrene (Graphite EPS)
This is an enhanced form of conventional EPS, where graphite particles are incorporated into the standard structure of expanded polystyrene. These graphite particles act as absorbers and reflectors of thermal radiation, reducing the thermal conductivity (λ) of the material compared to standard white EPS.
The addition of graphite gives the board a gray color, indicative of its different composition. As a result, the same level of insulation can be achieved with a thinner insulation layer compared to conventional EPS - offering up to 15%-20% better thermal performance than standard EPS.
The applications of Graphite EPS are almost identical to those of regular EPS, with the primary use in external thermal insulation systems for masonry, as well as in surfaces where low thermal conductivity and consistent performance under moisture exposure are required.
Mineral Wool (MW)
Mineral wool is a fibrous, inorganic thermal insulation material derived from volcanic rock (e.g., basalt) or other metamorphic rocks (e.g., amphibolite), which is spun into fine, cohesive fibers capable of trapping air.
This structure provides excellent thermal and acoustic insulation properties. One of the most notable advantages of mineral wool is its non-combustibility; it does not contribute to ignition or flame propagation, offering significant fire protection to a building.
Additionally, due to its open fiber structure that allows water vapor to pass through, mineral wool promotes breathability in the construction, reducing moisture accumulation.
Mineral wool is widely used in external thermal insulation systems, as well as in ceilings, roofs, and flat roofs, where both thermal insulation and fire resistance are required. It is also applied in interior walls, suspended ceilings, and partitions to enhance acoustic insulation between spaces.
Adhesive Mortars & Finishing Plasters
Equally important as the insulation boards in any complete external thermal insulation system are the adhesive mortars and finishing plasters. Adhesive mortars are applied to the insulation boards on one or both sides, ensuring strong adhesion to the substrate and uniform stress distribution.
At the same time, they contribute to the mechanical strengthof the system and its long-term stability, even under demanding climatic conditions. The finishing plasters serve as the final protective and aesthetic layer, providing resistance to weathering, moisture, and UV radiation. Additionally, they define the wall’s final texture and color, enhancing both the longevity and the architectural identity of the building.
Accessories - auxiliary materials
Ancillary materials play a critical role in any complete external thermal insulation system, ensuring proper application, mechanical strength, and long-term functionality of the ETICS (External Thermal Insulation Composite System).
Reinforcing fiberglass meshes, embedded within successive layers of mortar or organic materials, provide effective crack resistance and help distribute stresses evenly across the surface. Primers, applied before the final decorative plasters, improve adhesion, regulate substrate absorbency, and ensure a uniform final finish.
Additionally, plastic or metal mechanical anchors secure the insulation boards firmly to the structural surface (concrete, brick, fiberboards, etc.), reinforcing the overall strength of the system. Complementary components such as corner beads, drip edges, and expansion joints ensure precision in detail, edge protection, and proper water drainage, preventing damage and structural pathologies.
All these elements do not function independently but form integral parts of a well-designed, tested, and certified external thermal insulation system, which guarantees reliability, durability, and high technical performance over time.
Certified ClimaWall® systems by BIOCLIMA stand out as truly reliable ETICS on the Greek market. With systems such as ClimaWall® Classic, Premium, Extra, Mineral, and numerous possible material combinations to meet any climatic, structural, spatial, or aesthetic requirement - fully compliant with European and environmental standards and installed by professionals - they represent a sure choice for external thermal insulation.