Everything You Need to Know About Home Insulation

Types, materials, advantages, and benefits - all presented in a practical knowledge guide that will help you understand what you need and what to choose in order to upgrade your home.
Home insulation consists of a series of technical interventions, depending on the type of insulation selected, which improve the overall performance of the building by acting as a controlled barrier between the indoor environment and external climatic variations, ensuring stable living conditions. For this reason, insulation is considered one of the most important long-term investments for a modern home. Below, we examine the different types of insulation and their characteristics, the main thermal insulation materials used, and other related issues.
Although most people use the general term “insulation” to describe any form of building protection, it is important to clarify that there are several distinct types of insulation, and not all of them necessarily contribute to energy savings. When the goal is energy upgrading, we are referring exclusively to thermal insulation, whether internal or external.
Other forms of insulation include waterproofing and sound insulation. Waterproofing is essential for limiting moisture and its destructive effects on a building, while sound insulation is necessary for maintaining a calm indoor environment. However, none of these insulation types directly reduce heat losses. Understanding this distinction is key to selecting the right type of insulation, depending on the problem you want to solve.
Types of insulation and their advantages
There are five main types of insulation for a home. Although it is rarely necessary to apply all of them at the same time, they often work together or complement one another to achieve a comprehensive result.
Internal thermal insulation:
Internal thermal insulation involves installing insulating materials on the interior side of walls, including vertical internal masonry, beams, columns, and ceilings, in order to reduce heat losses to the external environment. It is commonly used in buildings where external intervention is not feasible, such as listed or heritage buildings, or apartment blocks with multiple ownerships. It is characterized by its immediate impact on thermal comfort and the ability to be applied room by room.
Waterproofing:
Waterproofing encompasses all techniques that prevent the penetration of water or water vapor into terraces, walls, ceilings, foundations, and roofs. It uses membranes, liquid-applied coatings, bituminous layers, or elastomeric systems to create a watertight barrier. Waterproofing is critical for protecting structural integrity, as water is the most significant factor contributing to building deterioration.
Its major advantage is the prevention of reinforcement corrosion. It also ensures long-term durability and stability of the building envelope, reducing future maintenance costs.
Sound insulation:
Sound insulation aims to reduce sound transmission through walls, floors, and ceilings by using specialized materials and systems. It is a key comfort factor in densely populated areas, apartment buildings, and workplaces.
It can address both airborne noise (such as speech or music) and impact noise (such as footsteps and vibrations), depending on the system applied. The benefits include improved quality of life, increased privacy, and better conditions for concentration.
Fire-protective insulation (Fire protection):
Fire-protective insulation includes materials and systems that delay the spread of fire, limit high temperatures, and maintain the integrity of critical structural elements. It is applied to steel structures, escape routes, service shafts, and areas requiring increased resistance to thermal loads.
It provides vital time in the event of a fire by protecting the load-bearing structure and facilitating safe evacuation. Its main advantage is the significant enhancement of safety for occupants and installations, while working harmoniously with thermal insulation façade systems, thus delivering multiple performance benefits.
How thermal insulation works
Thermal insulation refers to the set of construction measures taken to reduce heat transfer between the interior of a building and the external environment, as well as between internal spaces with different thermal requirements.
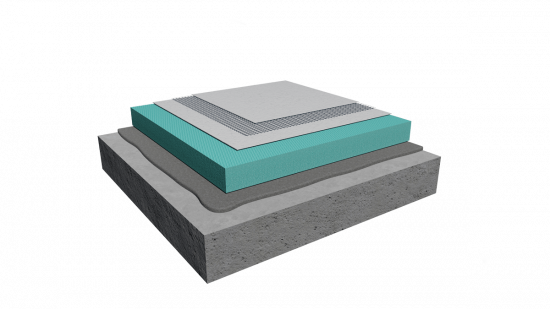
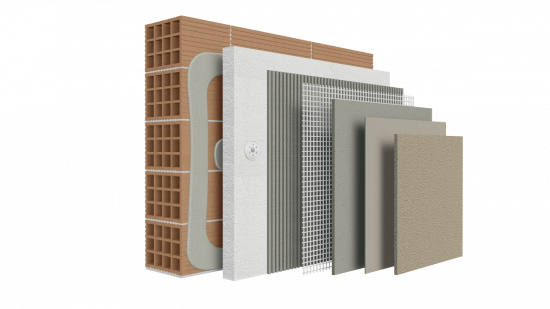
External thermal insulation (ETICS / Thermal façade systems): External thermal insulation - commonly referred to as a thermal façade—is applied externally to all sides of a building. It is considered the most effective solution for energy upgrading, as it protects the load-bearing masonry from extreme temperature fluctuations and takes advantage of the wall’s thermal mass.
It significantly improves the building’s energy performance, reduces heating and cooling demands, and enhances the aesthetic appearance of the façade. It provides long-term stability while simultaneously reducing the occurrence of moisture and mold. For these reasons, it is regarded as the most comprehensive solution for both existing and new buildings.
The most popular materials for home thermal insulation
At the core of every thermal insulation system lies the insulating material itself. These are specially engineered insulation products designed to meet requirements for thermal insulation, sound insulation, and fire resistance. Let’s take a look at the most fundamental categories.
Expanded Polystyrene (EPS Panels) is a lightweight, foam-based thermal insulation material with low cost, high thermal performance, and excellent long-term durability.
Graphite-Enhanced Expanded Polystyrene (EPS Graphite Panels) is a lightweight, foam-based thermal insulation material with low cost and high thermal performance—enhanced compared to standard white EPS—as well as excellent durability over time.
Extruded Polystyrene (XPS) is a synthetic material with a closed-cell structure. It is an excellent thermal insulator, distinguished by its high mechanical strength and resistance to moisture. For this reason, it has a wide range of applications, from foundations and floors to flat roofs and external walls.
Mineral Wool (MW) belongs to the category of inorganic fibrous materials and is derived from metamorphosed basalt rock. Through a specialized process and mineral enrichment, it is transformed into a material resembling rigid cotton wool. It provides excellent thermal insulation and sound insulation, high resistance to elevated temperatures (non-combustible up to +750°C), and a wide range of applications.
There are also additional products that work together within a thermal insulation system, whether for walls or roofs. These include waterproofing mortars, crack-resistant coats, fiberglass reinforcing meshes, and fixing accessories required for proper system installation.
When a House Needs Thermal Insulation
The need for thermal insulation becomes evident when a building exhibits significant heat loss, moisture problems, or unstable indoor temperatures. Warning signs include the appearance of mold on corners and walls (a phenomenon indicating cold spots and thermal bridges), as well as the sensation that the house “does not heat up” or “overheats” too quickly.
Older buildings with poor or non-existent insulation, as well as homes located in regions with very hot or very cold climates, are typical cases where thermal insulation is essential. In addition, high energy bills, condensation on windows and walls, or significant temperature differences between rooms indicate that the building envelope is not performing properly. Under all these conditions, thermal insulation acts as a critical - and often necessary - investment for comfort, hygiene, and the long-term durability of the home.
The Benefits of Proper Thermal Insulation
As outlined above, proper thermal insulation offers a range of immediate and measurable benefits: it significantly reduces heating and cooling costs, limits moisture accumulation and mold growth, enhances thermal comfort throughout the year, and improves overall indoor air quality.
At the same time, it protects the building structure from deterioration, maintains stable indoor conditions, and upgrades energy performance. In an environment of continuously rising energy costs, insulation is no longer a luxury but a strategic investment that delivers returns from the very first day.
If your home shows signs of wear or energy inefficiency, now is the right time to proceed with insulation and secure a more comfortable, safe, and cost-effective future.
If you are looking for a comprehensive and technically documented solution for insulating your home or roof, consider the certified BIOCLIMA ClimaWall® systems. Installed by specialists and fully compliant with European standards, they can significantly enhance energy efficiency, durability, and thermal comfort—while helping you save money.