Green Development: The new trend in Construction

Sustainability, energy saving, pleasant living and wellness. These are the 21st Century challenges - in building construction as well. The following are essential facts you need to know, from practices and benefits to certifications and recommended solutions.
Green development, also known as viable or eco - friendly construction, is a concept relating to building design, construction, operation & maintenance methods, aiming at the protection of the environment and efficient resources utilization.
Its core objective is minimizing the negative impact to the environment and the creation of healthy, comfortable living spaces for individuals, at the same time preserving balance with the nature. As “sustainability”, in conjunction with climate change, are nowadays perhaps the hottest words in the developed world. Green development is a powerful trend that will surely become inevitable.
Moreover, it refers to the entire building life cycle, from design to reconstruction, and necessitates collaboration between all battery development stakeholders, i.e. architects, engineers, contractors, interior designers, and agronomists.
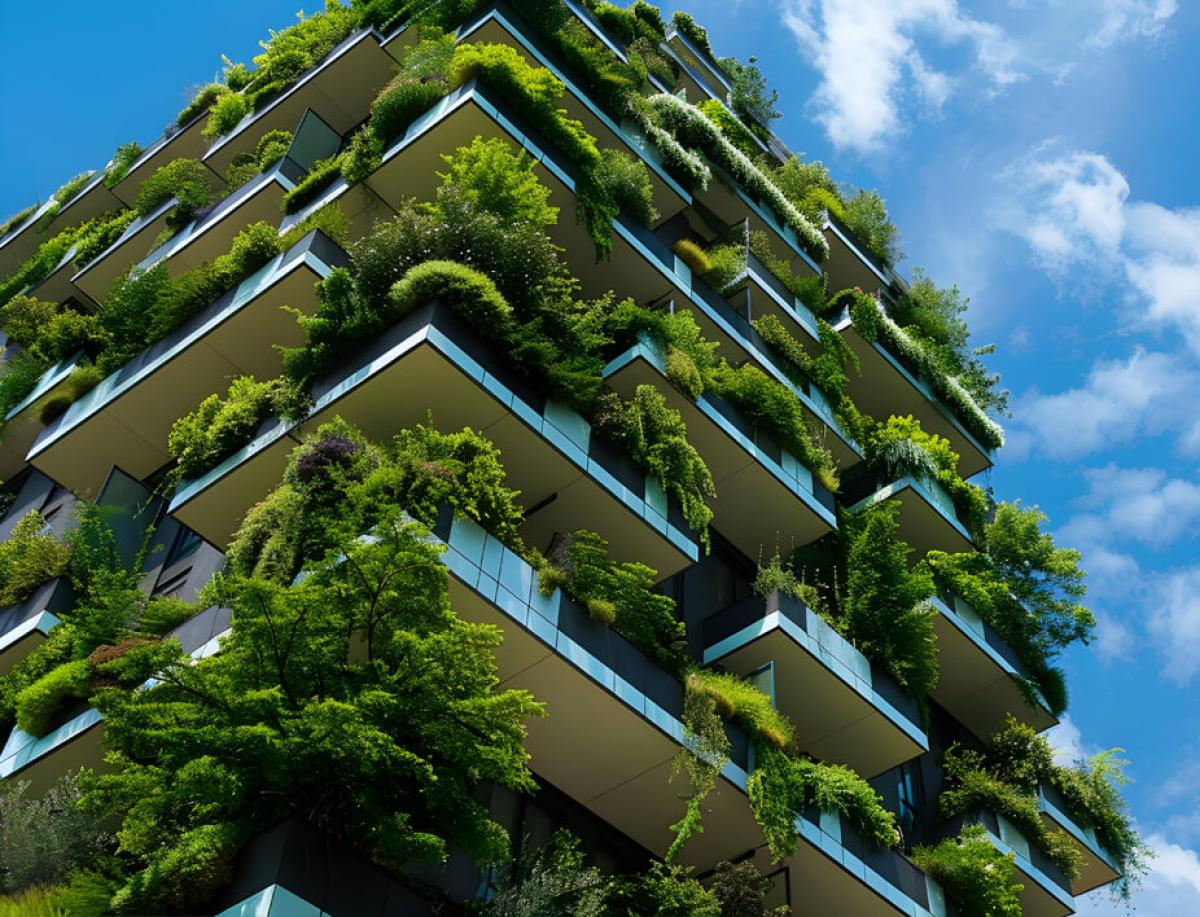

Key advantages of green development
Energy saving is a main advantage derived from the development of green buildings. Thanks to innovative technologies, such as thermal insulation systems, solar panels and energy efficient lighting systems, green buildings use less energy for heating, cooling and lighting.
Furthermore, they integrate smart energy management systems and make efficient use of natural resources such as solar light and heat for domestic requirements. This translates into significant reduction of energy expenses and mitigates greenhouse gas emissions, thus promoting sustainability. Sustainability and green buildings are an inseparable pair.
The architect’s role
Architects, being the main drivers in green building design, are obliged to focus on several factors, to successfully implement sustainability and environmental responsibility. Let’s examine the core features that an architect should consider.
Energy Efficiency: It examines the utilization of materials offering thermal insulation, those that improve building energy efficiency by decreasing consumption. For instance, architects plan the placement of windows to make use of natural light and to enhance space ventilation.
Water Resources Management:Architects apply storm water collection and recycling, contributing to the reduction of wasting water (a significant factor in times of water shortage). The collected storm water is stored in tanks, allowing its use for garden watering or washing; recycled water can be used in ornamental applications, e.g. water fountains.
Sustainable Origin Materials: Architects seek locally - procured and recycled materials, restricting the environmental footprint that would result due to their transportation. Architects also consider material life cycle times, ensuring that these materials are environment - friendly and long lasting.
Urban Integration: Architects consider the impact of buildings to the surrounding ecosystem and the local community, aiming at the development of properties that seamlessly blend and ameliorate the urban environment at large.
Renewable energy sources technologies: Architects integrate photovoltaic systems and various technologies to provide for energy production from renewable sources (RES).
Utilization Flexibility: Architects design buildings adaptable for multiple purposes (commercial, residential and more), extending their life cycle.
Basic green development practices
The following practices constitute basic conditions to build a case for green concept - based buildings. These are the pieces that, joined together, make up the overall picture.
Green Terraces and Patios: These practices contribute to the reduction of building temperature. They improve air quality, offer a cooler ambience, and free up green spaces that allow tenants to sit around and relax.
Storm Water Collection: These systems utilize storm water for non - drinking purposes, thus reducing requirements for additional water resources.
Material Recycling: Using recycled or recyclable materials results in less waste generated and a reduction in manufacturing cost.
Smart Design: It relates to optimal utilization of the building’s natural light and orientation to facilitate ventilation and reduce dependence from powered systems (e.g. bathrooms that use windows for ventilation, instead of fans).
Energy Management Systems: These relate to the installation of automated systems monitoring and optimizing energy usage in real time.
Low embedded energy materials: The overall environment impact of buildings is reduced using materials requiring less energy for their production and transport.
There are more interventions that indirectly relate to the green building concept (these are, by way of example, fermentation of organic waste; low power consumption household appliances and light bulbs, heat pumps, underfloor heating etc.). However, these are not directly linked to building, thus we will no more elaborate on these.
Standing legislation and international certifications
According to the green development legislation, essential codes are included in the 2012 New Building Code (ΝΟΚ) (Law 4067/2012). This sets forth energy efficiency regulation and describes the main prerequisites so that a building qualifies as green. Three years later, Law 4342/2015 harmonized the national legislation with the European Directive on energy efficiency (2012/27/ΕU), focusing on the upgrade of building infrastructure and the use of RES. These codes support the shift to green development, demanding compliance to energy performance standards for new and existing buildings.
Furthermore, green buildings often receive certification through standards that assess sustainability, energy efficiency and user well-being. The following are three well - known and reputable certification standards:
LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design): Developed by the U.S. Green Building Council (USGBC), it qualifies buildings in areas such as energy efficiency, water conservation, indoor environment quality and use of sustainable materials. LEED certifications are classified under discreet levels, Certified to Platinum, promoting resources efficiency and the reduction of environmental footprint
BREEAM (Building Research Establishment Environmental Assessment Method): It focuses on environmental performance throughout the building’s life cycle. It employs features such as energy, materials, health and comfort, as well as waste management. It was developed in the UK by the BRE; it offers certification levels varying from Pass to Outstanding.
WELL Building Standard: This is the most people - centered standard. It mainly focuses on user health and well-being, assessing air, water, comfort, lighting and design solutions that promote mental health. WELL, an American standard, promotes productivity and living quality improvement for the examined buildings.

Solutions available in the marketplace
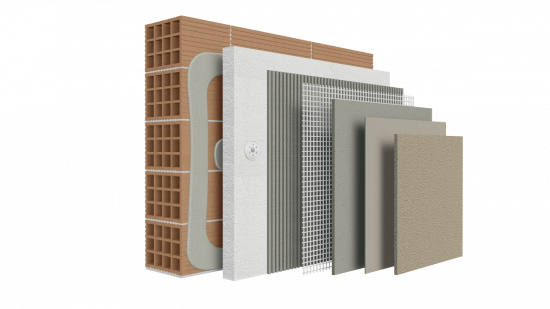
Browsing the domestic market and proposals that could support a green building project, one that would particularly stand out is BIOCLIMA®, a solution guaranteed by KRAFT Paints, the first Greek company awarded with Environmental Product Declaration (EPD) for its certified ClimaWall® Exterior Wall Thermal Insulation System. This way, the company contributes to sustainable development and actively supports the improvement of structure ratings through internationally recognized standards (LEED, BREΕAM, WELL etc.), being a participant to the corresponding adjustments.
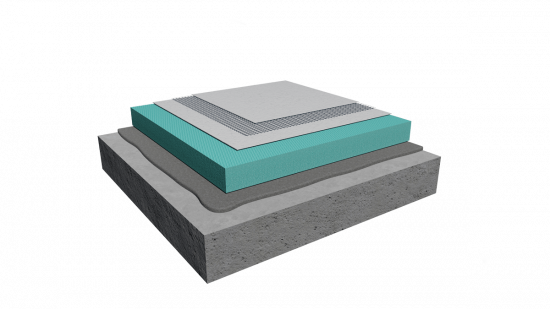
The certified exterior wall thermal insulation system combinations ClimaWall® of BIOCLIMA® (comprising of successive layers of individual products) have been evaluated by Accredited European Laboratories notified to ΕΟΤΑ (European Organization for Technical Assessment), according to the EAD 40083-00-0404 Standard, and with the 4 popular thermal insulation boards signed by BIOCLIMA: Expanded Polystyrene (white & gray), Extruded Polystyrene and Rock Wool. The same applies to BIOCLIMA ClimaRoof® , an integrated lightweight, thermal & water insulation system for flat roofs (terraces).
Furthermore, individual BIOCLIMA products are backed by all the necessary certifications to meet the applicable European and national norms on green development. Thus, these are worth paying attention to as well.